
GAS CONSTANT IUNIT ISO
When using the ISO value of R, the calculated pressure increases by only 0.62 pascals at 11,000 meters (the equivalent of a difference of only 0.174 meters, or 6.8 inches) and an increase of 0.292 pascals at 20,000 meters (the equivalent of a difference of only 0.338 meters, or 13.2 inches). Thats because the SI unit of volume is the cubic metre, m3 - not cm3 or dm3. This disparity is not a significant departure from accuracy, and USSA1976 uses this value of R for all the calculations of the standard atmosphere. Gases are made up of molecules which are in constant random motion in. The USSA1976 does recognize, however, that this value is not consistent with the cited values for the Avogadro constant and the Boltzmann constant. The gas constant occurs in the ideal gas law (the simplest equation of state) as follows: The molecules of an ideal gas are often compared to rigid but elastic billiard balls. Additionally, the molecules or atoms of the gas have complete randomness of direction and velocity, and they undergo perfectly elastic collisions with the walls of the container. Ideal gas lawĪn ideal gas (or "perfect" gas) is a hypothetical gas consisting of a very large number of identical particles, each of zero volume, uniformly distributed in density, with no intermolecular forces. The gas constant is a factor in the ideal gas law, which provides an approximation of some of the properties of gases. Movement of particles ( atoms, molecules, or ions) in the gas phase. The two digits in parentheses indicate the uncertainty (standard deviation) in the last two digits of the value. It is equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, except that the latter is expressed in units of energy per kelvin per particle.ĭenoted by the symbol R, the value of the gas constant is:
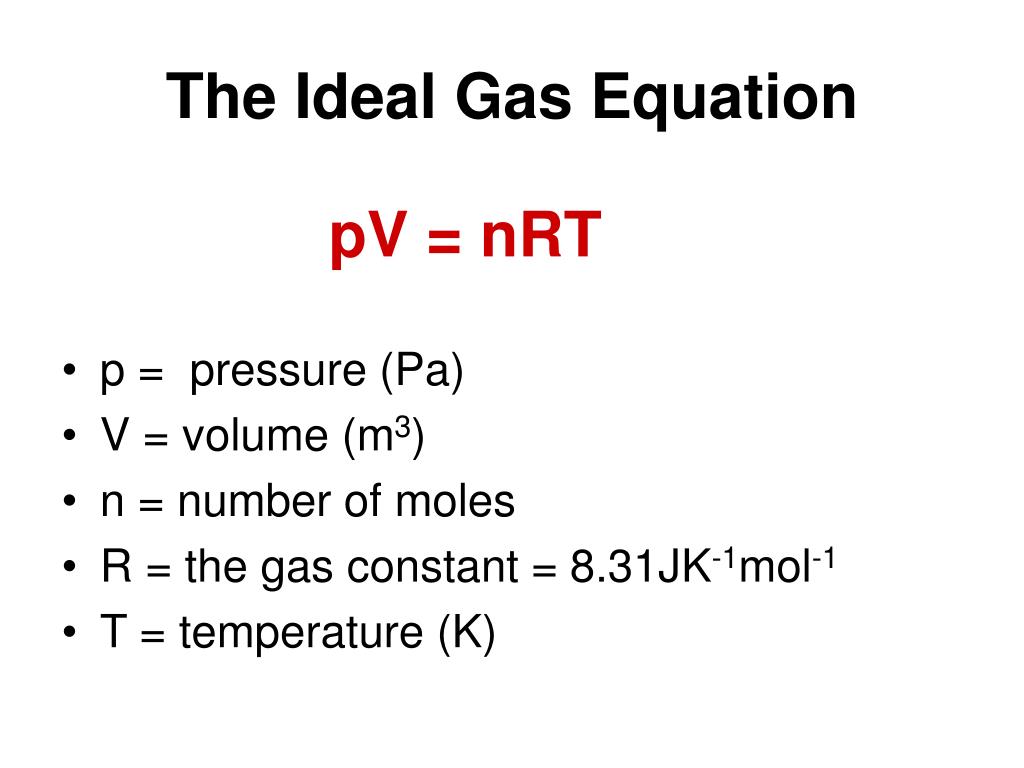
The unit for the gas constant is the joule per mol-kelvin. It is expressed in units of energy (that is, the pressure-volume product) per kelvin per mole. The currently accepted value for the universal gas constant R is: R Constant 8.3144598 J/molK. I hope you understand the solution.The gas constant (also known as the molar, universal, or ideal gas constant) is a physical constant that is featured in a number of fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law and the Nernst equation.

Okay, so the correct answer is option number D. This is the unit of working as a unit of work done is jewel as well. And this entity is basically june this is the unit of Brooklyn. So this will give newton meter divided by mold, multiplied by Calvin. You divided by mole animal deployed by building. Now when will put these values? So are you will be newton per meter square multiplied by matrix. Ideal gas law - Boltzmann constant - Avogadros law - Nernst equation - Temperature - Heat capacity - Entropy - Physical constant - Henri Victor Regnault - Pressure - Thermodynamic temperature - Avogadro constant - Speed of sound - U.S. 08206 because we will we will be calculating either L, atm, mol or K. If we are calculating using the ideal gas equation PVnRT then we use the. Example files: linearnet, branch1, branch2. This value is appropriate for air if Joule is chosen for the unit of energy, kg as unit of mass and K as unit of temperature, i.e. However, if we express R in units of L atm/mol K, its value is 0.08206. defines a specific gas constant with a value of 287. It's newton permit re square as a uniter and which is mall is M. In SI units, the real gas constant, R, is equal to 8.3145 Joules/mol K.

Right? As a unit of volume is meter cube. Oh pressure is as a unit of pressure is newton meter. Answer (1 of 6): Values of gas constant in different units are as follows 8.3145 J K-1 mol-1 62.364 L Torr K-1 mol-1 8.31451 x 10-2 L bar K-1 mol-1 8.31451 Pa m3 K-1 mol-1 8.20578 x 10-2 L atm K-1 mol-1 1.

The most commonly used value is 8.3145 J/molK. Unit for gas constant varies depending upon other units used in the equation. Is the volume and its number of moles and T. The relationship of universal gas constant with Boltzmann’s constant can be expressed as R k B N A Gas constant in different units. they are related in the ideal gas equation. If you continue browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this website. The concentration of a gas phase reaction is n/V. Value of R (Universal Gas constant) in various Units SlideShare uses cookies to improve functionality and performance, and to provide you with relevant advertising. This is only done if the system at question is a gas phase reaction. So for this we will use the ideal gas equation which is T. Answer: Use whichever one you need to cancel the units of pressure and get units of concentration. So in this question we have to find the S.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
